Implementing Three.js within a React.js application involves integrating the 3D rendering capabilities of Three.js with the component structure of React. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you set up a basic scene with Three.js in a React project:
For reactjs new comers, please check the below link:
1. Set Up Your React Project
If you haven’t already created a React application, you can start one using Create React App:
npx create-react-app my-threejs-project cd my-threejs-project
2. Install Three.js
You need to add Three.js to your project:
npm install three
3. Create a Three.js Component
You can create a Three.js component that handles the setup of the scene, camera, and renderer. Here’s an example of how you might set it up:
import React, { useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
import * as THREE from 'three';
const Scene = () => {
const mountRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
// Scene
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xabcdef);
// Camera
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
camera.position.z = 5;
// Renderer
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
mountRef.current.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// Adding a cube
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry();
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(cube);
// Animation loop
const animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
cube.rotation.x += 0.01;
cube.rotation.y += 0.01;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
animate();
// Handle resizing
const handleResize = () => {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
};
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
mountRef.current.removeChild(renderer.domElement);
};
}, []);
return <div ref={mountRef} />;
};
export default Scene;
4. Integrate the Three.js Component in Your App
Now, integrate this component into your React application by including it in your main App component:
import React from 'react';
import Scene from './Scene';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<Scene />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
5. Run Your Application
Start your application to see the Three.js scene:
npm start
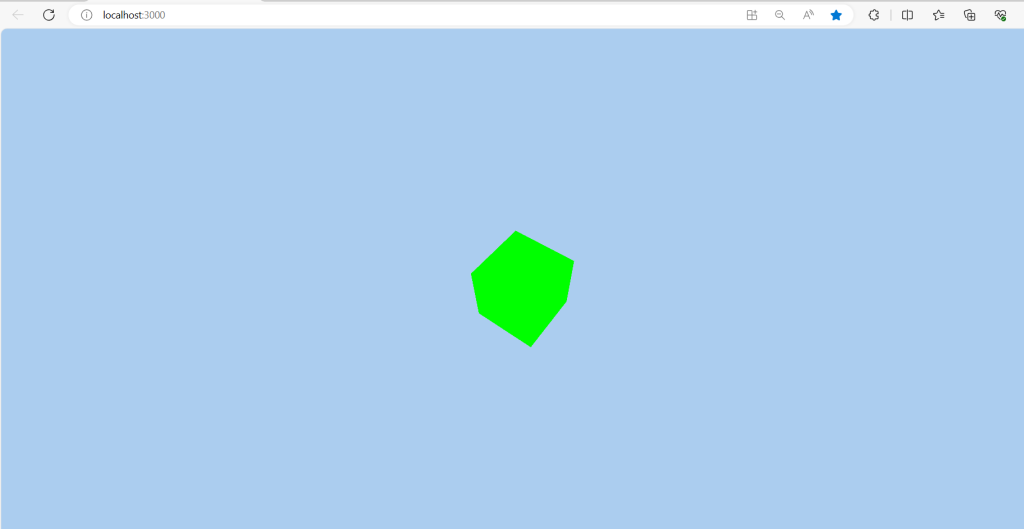
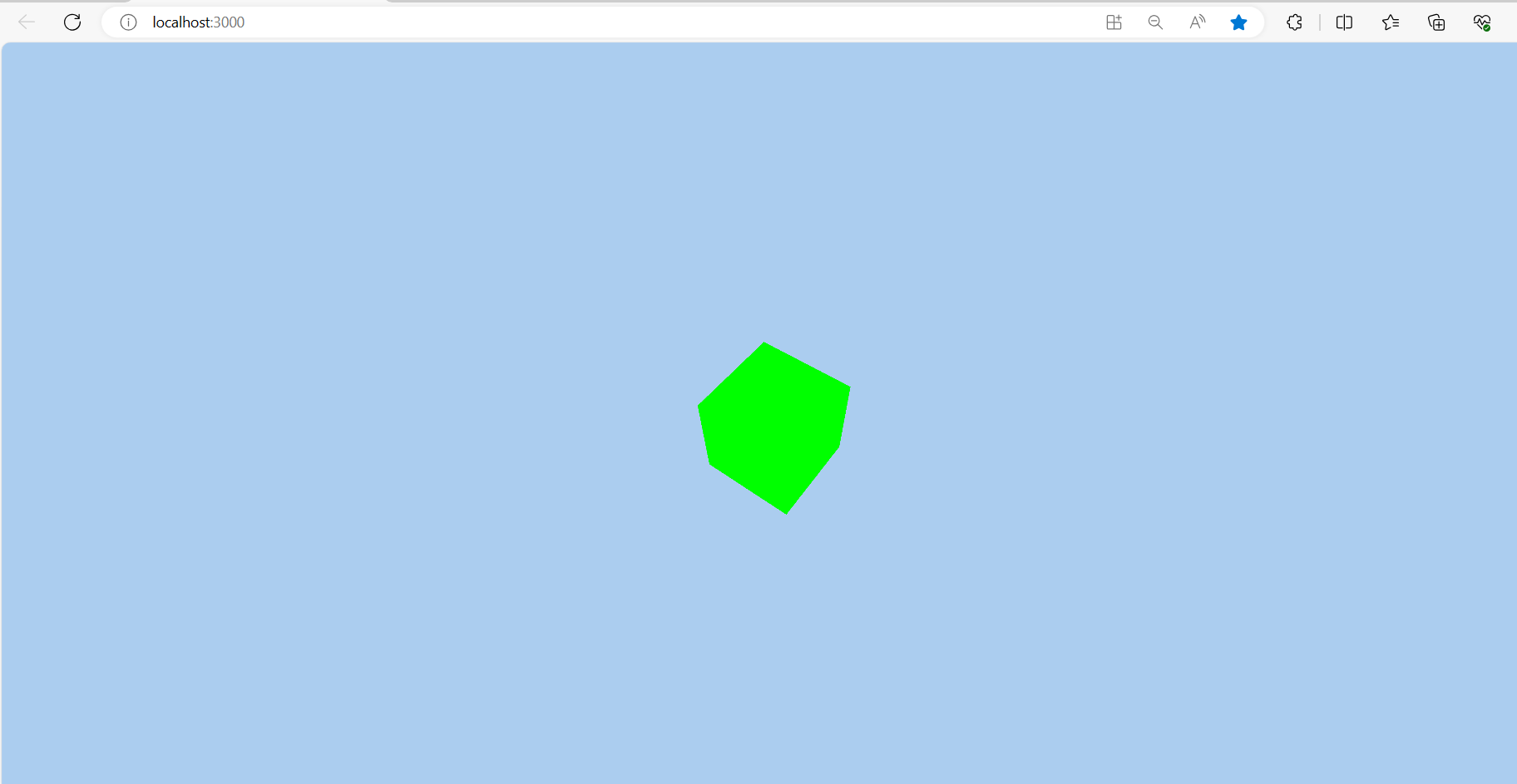
This setup provides a basic Three.js scene with a rotating cube in a React application. You can extend this by adding more complex objects, lights, and shadows to create richer visual effects.
Jaasa
Thanks
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.